ETH Zurich is looking for a licensing or collaboration partner for PEGylation of therapeutic proteins and peptides.
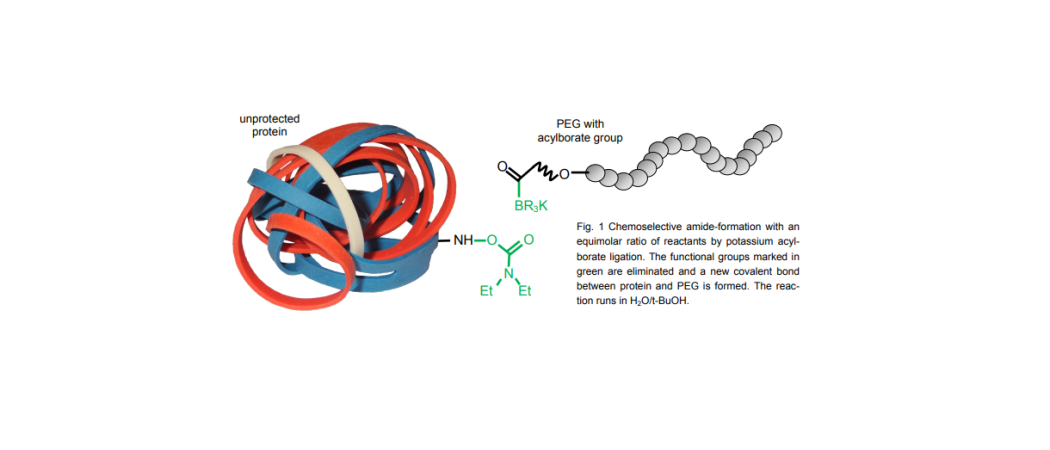
Hydroxylamines and acylborate compounds give access to the fast, selective and convenient covalent ligation of large biomolecules as used for antibody drug conjugates.
Most organic reactions require anhydrous, organic solvents and do not operate properly in the presence of unprotected organic functional groups. Joining large molecules is typically a slow reaction, requiring high concentrations, long reaction times, a large excess of one reactant, and/or high temperatures.
O-substituted hydroxylamines and potassium acylborates undergo a rapid, selective reaction to form amide bonds. This reaction operates in water and is not disturbed by the presence of unprotected amines, acids, alcohols, thiols, etc. It allows two large molecules to be selectively joined together by an amide bond using a 1:1 ratio of the reactants. The acylborates are new functional groups and have proven to be surprisingly stable and easy to handle.
Features & Benefits
- Equimolar reactants
- High second-order rate constant in aqueous solutions
- Chemoselectivity in the presence of unprotected functional groups
Fields of Application
- Selective formation of a covalent bond between two large molecules
- Synthesis of PEGylated biomolecules
Patent Status
- EU and US patents granted; JP nationalization
Publication
- White C.J., Bode J.W., “PEGylation and Dimerization of Expressed Proteins under Near Equimolar Conditions with Potassium 2-Pyridyl Acyltrifluoroborates”, ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 197−206




 A unique international forum for public research organisations and companies to connect their external engagement with strategic interests around their R&D system.
A unique international forum for public research organisations and companies to connect their external engagement with strategic interests around their R&D system.