Robots are beginning to work safely hand in hand with staff on industrial shop floors, without the need for fences, thanks to two projects funded through Factories of the Future, EFFRA’s partnership with the European Commission on manufacturing
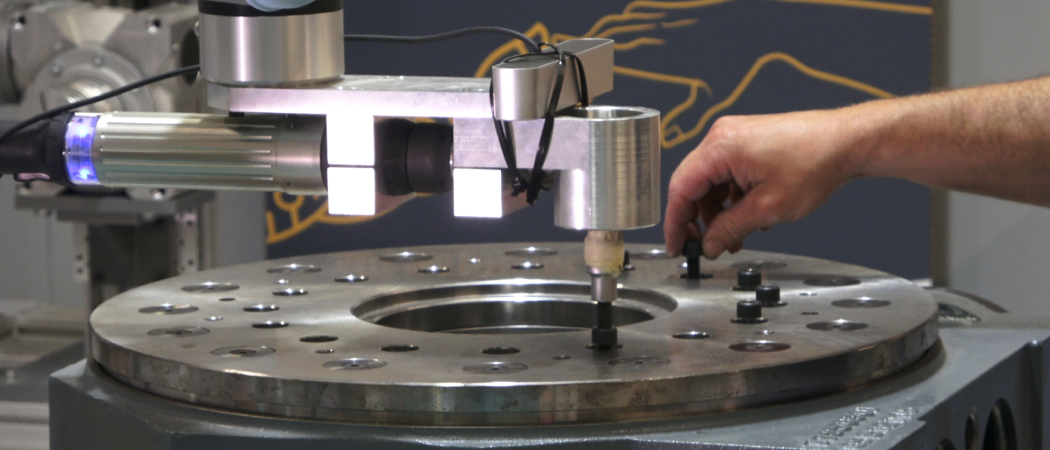

Sharework, a project led by Eurecat Technology Centre, has developed 14 integrated software and hardware mechatronics modules that provide robots with the intelligence they need to work alongside human operators and overcome human-related barriers. The modules cover the areas of perception, motion planning, safety and security, and multimodal human-robot communication, including knowledge of object detection, person tracking, and human task identification through environment run-time detection and cognition.
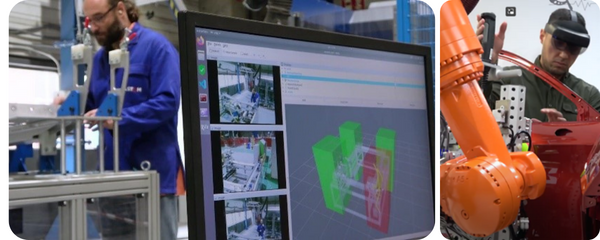
“By allowing operators to share or delegate the simple and repetitive operations to robots, while ensuring safety in the work environment and getting additional assistance from the system to improve ergonomics, Sharework contributes to increasing the OECD Job Quality Index through an improvement in the work environment and safety,” says Dr Néstor Garcia, the technical coordinator of the Sharework project, a Factories of the Future project funded by the European Commission Horizon 2020 programme. “Therefore, collaborative robotics can reduce workers’ physical stress and healthcare risks, and improves their satisfaction.”
Collaborative robotics is one of the shared technological challenges being tackled by the European Factories of the Future Research Association (EFFRA), in part through its partnerships with the European Commission: Made in Europe and its predecessor Factories of the Future. Promoting precompetitive research and encouraging the collaboration between diverse international stakeholders at the industry and research levels, EFFRA is addressing all aspects of manufacturing, from sustainability and efficiency to digitalisation and human aspects; many of these demonstrators, use cases, and exploitable results, can be consulted by accessing EFFRA’s Innovation Portal, where innovation actors are invited to promote their work.
Demonstrating seamless and safe industrial human-robot collaboration
The solutions developed by Sharework have been successfully validated in four industrial environments. In the transport sector (ALSTOM), Sharework has been implemented in a railway rolling stock’s assembly line to assist workers in a static position in assembling and riveting parts during the manufacturing process. In the automotive sector, the project has installed and tested a collaborative high-payload robot to help an operator carry and position car components for assembly (SEAT S.A.). In other sectors, Sharework collaborative robots’ modular solution has been deployed via the provision of robots with the necessary knowledge to perform quality checks and provide support to operators in assembling and disassembling complex parts, reducing workers’ ergonomics’ effort (Goizper Group), as well as assisting the worker when moving across the station, while understanding workers’ behaviour and anticipating tasks (Cembre Spa.)
.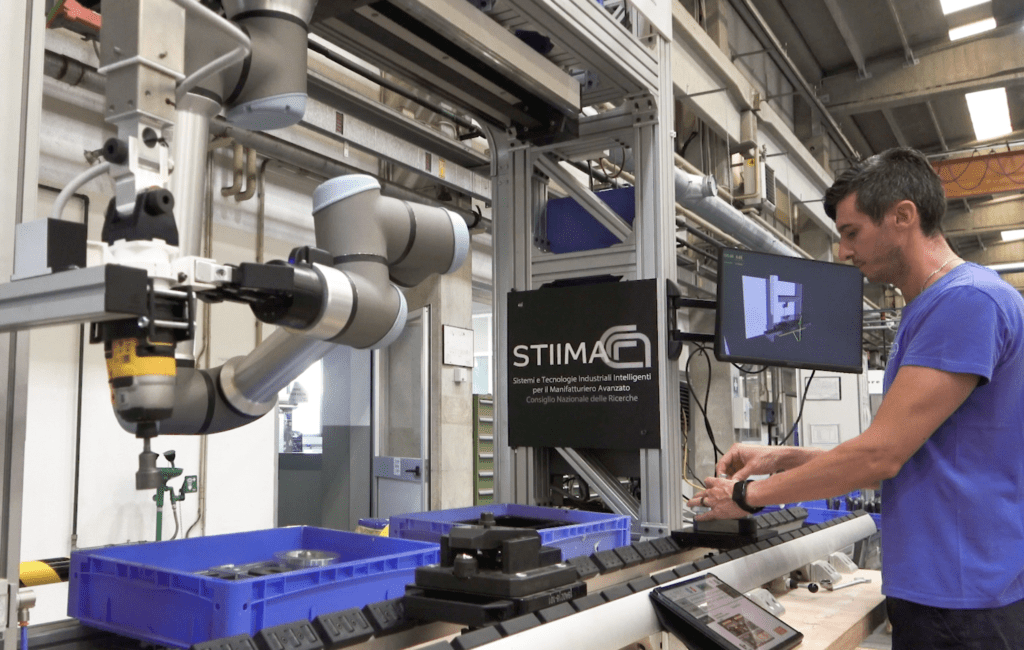
The complementary SHERLOCK project aimed to introduce the latest safe robotic technologies, including high and low payload collaborative arms, wearable robotics in form of exoskeletons and mobile manipulators, enhancing them with smart mechatronics and AI-based cognition. In so doing, the project is creating efficient and safe human-robot collaboration stations that are accepted by operators and are designed to ensure their wellbeing. SHERLOCK has developed a portfolio of 19 software and hardware modules covering key areas, such as collaborative production station and mechatronics, human-centred interaction and awareness, artificial intelligence enabled human-robot collaboration, safety and certification, which have been applied in four different industrial use cases.

In the renewable energy sector (CALPAK), a high-payload collaborative robot can lift and manipulate heavy solar panels. To reduce the repetitive tasks in the industrial modules assembly sector, in VDL, a new low payload-inverted collaborative robot has been tested to collaborate with the operator via an advanced digital twin that can perform on-the-fly task planning using data from a network of distributed sensors. In another scenario with FIDIA, enhanced augmented reality has been applied to the machine building sector to allow the operators to perform the assembly of large CNC (computer numerical control) machines. Finally, a new mobile robot equipped with two collaborative arms has been employed for the collaborative transportation of large composite parts in the aeronautics sector (SOFITEC).
“The self-adapting robots of SHERLOCK have managed to demonstrate seamless human-robot collaboration in four industrial scenarios, says Nikos Dimitropoulos from the Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems and Automation (LMS), coordinator of the SHERLOCK project. “In simple terms, the SHERLOCK robots were able to adopt a human-like behaviour, being valuable co-workers, understanding the environment, the needs and preferences of the operators, predicting human intention and adapting their behaviour accordingly, thanks to the advances in perception and AI-driven decision making.”
Putting workers’ well-being at the centre of innovation
Human centred design implies an explicit understanding of the operators and must include co-creation and iterative continuous user-centred evaluation. To do that, a multidisciplinary approach is fundamental and includes the participation of social science and humanities beyond the technical areas capable of deploying the intelligence required to implement the collaboration.
Sharework and SHERLOCK have delved into the interaction of social sciences and robotics to work towards reducing the stress of operators during assembly and disassembly processes, as well as to reduce the number of non-added-value repetitive tasks. Both systems have demonstrated gains in performance, ergonomics, a reduction of assembly errors, human stress, and high levels of operator acceptance, unveiling the real-world potential of highly intelligent assistive robotic systems.
“People are the most valuable asset in European manufacturing. We feel the need to keep them in the loop with an active and leading role, bringing technology around them to provide active support,” says Dr Sotiris Makris lead of the Robotics, Automation and VR in Manufacturing group of LMS. “Hybrid production systems, involving both mechanics in the form of smart robotics and advanced digital technologies, pave the road towards a human-centric, sustainable, resilient and green industry, augmenting the capacity of personnel and enhancing the competitiveness of EU manufacturing.”
Manufacturing is often regarded as a physically demanding industry, which could often exclude a large pool of potential workers; in this sense “collaborative robotics, when applied in industrial environments, present a great potential for supporting the workers and strengthening the European industry, opening up the shopfloors for greater gender and diversity inclusion, a step forward the factories of the future,” concludes Dr Simona Neri, project manager and coordinator of the Sharework project.




 A unique international forum for public research organisations and companies to connect their external engagement with strategic interests around their R&D system.
A unique international forum for public research organisations and companies to connect their external engagement with strategic interests around their R&D system.